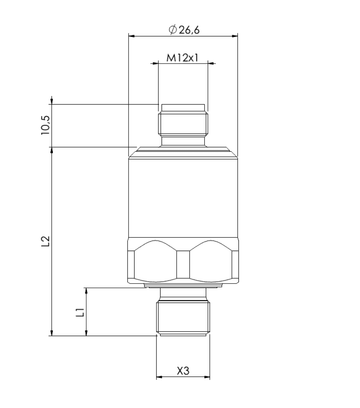
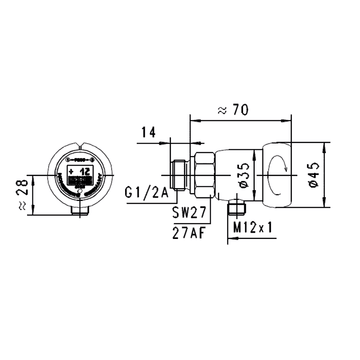
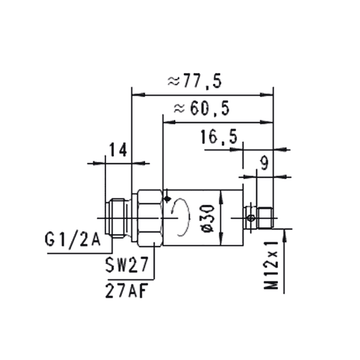
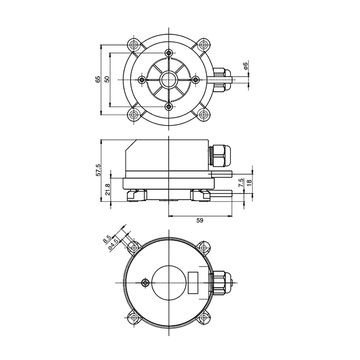
Pressure Sensors
A pressure sensor detects, monitors, reads, and displays changes in applied pressure from a restricted volume of liquid or gas. They may also be used for unconfined volumes such as atmospheric pressure. Pressure sensors are offered for various functions, circumstances, and applications.
How Does a Pressure Sensor Work?
As the name indicates, a pressure sensor is a kind of electronic measuring equipment used to detect and record changes in applied pressure.
The basic functionality of a pressure sensor requires any proportional change in applied pressure to cause a physical reaction in the device's sensing element.
This produces an output voltage, which may be conditioned (adjusted for environmental characteristics) and supplied as analogue or digital output signals. These readings vary as additional pressure changes are recorded, allowing for continuous monitoring of applied pressure over time.
What Are the Uses of Pressure Sensors?
Pressure sensors are widely used in various applications in several industries and sectors.
Pneumatic pressure sensors assess air or gas pressure changes, while hydraulic pressure sensors monitor water or fluid pressure changes.
Common pressure sensor applications include:
- Checking the applied pressure (or measuring the minimum and maximum pressures) of various gases and liquids housed in sealed tanks, containers, and systems.
- Determining flow rate and direction by observing pressure differences between two or more locations
- Analysing variations in atmospheric pressure (i.e. barometric pressure) for environmental or navigational purposes
Pressure sensors, pressure transducers, and pressure transmitters all have a pressure detecting element, but each translates and conditions the output signal from that element in somewhat different ways.
In any case, the broad term pressure sensor might refer to any of these three device types:
1. Pressure Sensors
A physical reaction in the sensor module provides an output signal in a genuine pressure sensor. Further signal conditioning, such as calibration, amplification, and temperature correction, must be conducted separately before readings may be considered trustworthy and reliable.
2. Pressure Transducers
Pressure transducers, like pressure sensors, provide an output voltage due to the sensing element's physical reaction. The key difference is that the transducer also performs signal conditioning, allowing them to be transmitted farther away from the source.
3. Pressure Transmitters
A pressure transmitter works the same way as a transducer, except that instead of measuring voltage, it sends a current signal over a low-impedance load (often somewhere in the 4-20mA standard industrial range).
Types of Pressure Sensors
The three main types of pressure sensors are absolute, differential, and gauge. The best kind of sensor to buy in any given case depends entirely on the nature of your application and the sorts of readings you want to make.
1. Absolute Pressure Sensors
Absolute pressure sensors are classified as vacuum pressure sensors. In contrast to others, their measurements are always relative to zero, and their output values are always positive. They can measure air pressure in barometer-critical applications like weather monitoring and navigational altitude detection. Barometric pressure sensors rely on an absolute vacuum to provide a baseline value for reliable readings. Because a gas's pressure is inversely proportional to its temperature, this is crucial for barometer detection. If a perfect vacuum was not employed as a zeroing reference, absolute pressure readings would change with heat fluctuations.
2. Differential Pressure Sensors
Differential pressure sensors measure the pressure differential between two points in a system. This is required to ensure the appropriate functioning of numerous system components, such as release valves and flow rate. Differential pressure sensors have varying specifications but usually sense pressure on each side of a single diaphragm in the sensor element. Depending on how the pressures distort the diaphragm, the values on either side may be positive or negative.
Alternative setups that detect pressure difference between two or more separate sensor devices positioned distantly and connected by signals from their internal electronics may be constructed.
3. Gauge Pressure Sensors
A gauge pressure sensor is a relative pressure sensor. They are often used to compute the pressure differential between the local air pressure and the pressure level at a certain point in another system.
Examples of uses include checking the fluid levels in a vented tank, operating blood pressure monitors, and controlling the desired speed and power of a vacuum pump. Differences in local air pressure around the system will change the calculations and measurements required in both circumstances.
Many gauge sensors use a membrane that is coupled to a resistor or other electrical device that records deflection forces as a change in output value.
PVL Pressure Sensors
Pressure Vacuum Level Ltd has been selling high-quality pressure sensors for over 28 years. PVL provides these devices for various industries.
Don't hesitate to contact us if you have any questions about our pressure sensors or other products.
Other Products
PVL customers can rely on us for high-quality products. Pressure Sensors are only a handful of the products we provide customers across the United Kingdom. We are also a significant supplier of Pressure Switches and Transducers.
- Grivory, Industry First, Lightweight
- Connects to smart phones and tablets with BLE (Bluetooth® Low Energy)
- Remote Monitoring Capability Available
- Pressure ranges up to 1,000 psi 1% Standard accuracy
- Long battery life
- Alarm set points
- Secure field programmable naming
- Patent Pending Design
- Electronic Pressure Transducer
- 4-20mA transducer
- 0-400 bar measuring ranges
- Over-pressures up to 650 bar
- M12 electrical connector
- 1/4” BSP standard thread
- 316L stainless steel
- Pressure Transducer System with Switch Points
- Up to 400 bar measurement range
- Over-pressures up to 600 bar
- Analog output, two switching outputs
- 1/2” BSP thread
- Back Lit LCD display
- Easily adjustable
- Wireless Bluetooth Pressure Transducer
- The first Bluetooth wireless pressure transducer
- Connects to smart phones and tablets with BLE
- Pressure ranges from Vacuum to 10,000 psi
- Stainless Steel
- All wetted parts 17-4 PH Stainless Steel
- Minimum IP rating of IP65 in accordance with BS EN 60529:1992.
- Frequency Response: <1ms for Conditioned Outputs
- Maximum Current Draw : 2-wire Transmitter = 20mA, Transducer in voltage mode = 4.5 mA
- EMC Data: Meets the requirements of CE.
- Connects to smart phones and tablets with BLE (Bluetooth® Low Energy)
- Certified Bluetooth® Wireless technology
- Pressure ranges from Vacuum to 10,000 psi
- Long battery life (proprietary technology)
- 1% Standard accuracy with optional 0.25% Ultra high accuracy
- Stainless Steel and high impact polycarbonate construction
- Alarm set points
- Secure field programmable naming
- Differential pressure measurement for non-aggressive gases
- Short reaction time
- Analog output, two switching outputs
- Clear, easily legible, illuminated LCD display
- Designed for industrial use
- Small, compact construction
- Very simple installation
- Control panel assembly (IP65)
- Sensor: Ceramic Element
- Response Time: ≤ 4 ms
- Tightening Torque: 30 Nm
- Protection Degree: IP 67
- Supply Voltage: 8÷30 Vdc
- Current Consumption: ≤ 25 mA
- Temperature Ranges: 0÷80°C, -20÷80°C
- Life expectancy: > 10 million cycles
- Weight: 86g
- Pressure Transducer With Switch
- Up to 400 bar pressure range
- Over-pressures up to 600 bar
- 4-20 mA or 0-10 V DC
- 1/2” BSP thread
- IP67 Rated
- Switching output and/or analogue output
- Programmable Pressure Converter
- Up to 2000 mbar measurement range
- Max over-pressure 4000 mbar
- 4-20 mA Outputs
- 4 mm pressure tube connection
- Programming via front side keypad
- For dry and non aggressive gases
- All Stainless Steel Wetted Parts for Maximum Media Capability
- Industrial Grade Pressure Transducer
- Overpressure protection to 3x
- Vac to 285 psi or 3 to 10,000 psi Range
- 9.4 Mini Din and Packard Electrical Connectors
- Better 0.4% Accuracy
- Custom Outputs and Ranges Available
- CE, RoHS, REACH, and Prop 65 Compliant
- All Stainless Steel Wetted Parts for Maximum Media Compatibility
- Industrial Grade Pressure Transducer
- Overpressure protection to 3x
- Vac to 285 psi or 3 to 10,000 psi Range
- 9.4 Mini Din and Packard Electrical Connectors
- 1% Accuracy
- Custom Outputs and Ranges Available
- CE, RoHS, REACH, and Prop 65 Compliant
- Total Digital Design Pressure Transducer Voltage and Current outputs
- Custom pressure ranges and outputs available
- Spike Monitoring Technology
- 24V Digital Output
- Low Current Consumption
- Differential Pressure Transmitter for Air Up to 250 kPa pressure ranges
- Manual/automated offset compensation
- 4-20 mA or 0-10 V DC output
- 6.0 mm Ø push-on tube connection
- mbar or pascal pressure units
- Optional LED display